Health
7 Causes of AFIB
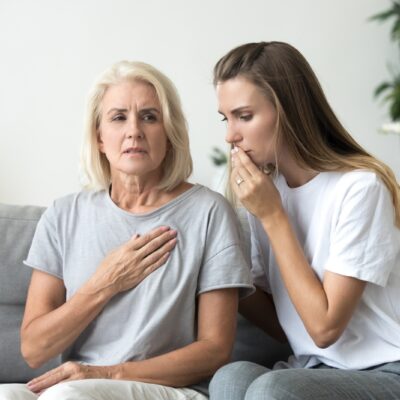
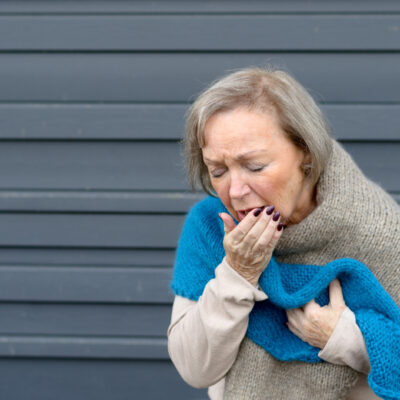
AFIB, short for atrial fibrillation, is a prevalent heart rhythm disorder that demands attention due to its potential impact on cardiovascular health. If you’re grappling with AFIB symptoms or seeking insights into its causes, this article is your comprehensive guide. We begin with heart diseases, a critical factor in AFIB, and include a deeper look into other contributing factors. Additionally, we’ll highlight the significance of AED machines in emergencies and provide insights into symptom recognition and advanced treatment options. 1. Heart Diseases Heart conditions, notably valvular heart diseases, play a central role in the onset of AFIB. Issues such as mitral valve prolapse, rheumatic heart disease, or aortic stenosis disrupt blood flow and electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat. These structural and functional changes in the heart predispose individuals to AFIB. For managing such diseases, treatments range from medications to manage symptoms to surgical interventions like valve repair or replacement when necessary. Valve replacement surgery, in particular, involves replacing a damaged valve with a prosthetic one to restore normal heart function and rhythm. 2. Age and Aging Aging is a natural contributor to AFIB as the heart’s electrical system experiences wear and tear over time. As we age, changes in cardiac tissue and a decline in the efficiency of the heart’s electrical pathways increase the likelihood of developing atrial fibrillation.
Read More